Commonly Infected Wildlife
Numerous species of fish can be affected.
Is This Animal Infected?
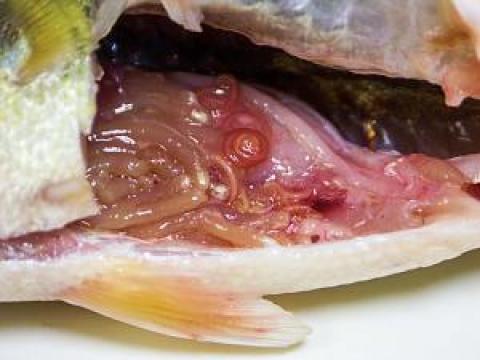
Red, off-white, and white worms found under the skin, in the intestines, and in the body cavity.
Can I Get It?
No. Presently, there is no known transfer to humans from U.S. freshwater game fish.
How Bad Can It Get?
Humans are typically not at risk for fish roundworms in U.S. freshwater game fish.
Symptoms in Humans
None. People are typically not at risk.
Andy Goodwin
Protect Myself and Others
Consume fish fillets like any other, by properly cleaning, preparing, and cooking the fish to 145°F.
Safe for Pets?
Yes. There is no known health risk when fish are properly cooked.
What Causes It?
A variety of nematodes (roundworms) live in fish during various stages in their life cycle. Commonly seen roundworms include camallanus, philometra, and contracaecum. Roundworms such as anisakis can infect humans, but they are found in marine fish.